CTF writeup: The Greenholt Phish (TryHackMe)
Link to challenge: The Greenholt Phish
The task
A Sales Executive at Greenholt PLC received an email that he didn’t expect to receive from a customer. He claims that the customer never uses generic greetings such as “Good day” and didn’t expect any amount of money to be transferred to his account. The email also contains an attachment that he never requested. He forwarded the email to the SOC (Security Operations Center) department for further investigation.
Investigate the email sample to determine if it is legitimate.
Let’s launch the machine and dive right in!
Task 1: What date was the email received? (answer format: M/DD/YY)
First, let’s fire up a termianl and cd our way into /home/ubuntu/Desktop. Now let’s run head challenge.eml to get the first 10 lines of the file wich should contain the date.
In fact, it does!
A: */**/2020
Q2: Who is the email from?
By running grep -i "from" challenge.eml we can get the relevant message headers. Our answer can be found on line 7.
A: Mr. J*** J***
Q3: What is his email address?
Answer can be found on the same line as the answer to the previous question.
A: info@muta***.com
Q4: What email address will receive a reply to this email?
Run command grep -i "reply-to" challenge.eml. Boom!
A: info.muta***@mail.com
Q5: What is the Originating IP?
Answer can also be found in the same output as question 2 and 3, but on line 5 this time. Rerun the command grep -i "from" challenge.eml to get the output.
A: “192.***.**.***”
Q6: Who is the owner of the Originating IP? (Do not include the “.” in your answer.)
To get the answer I did a lookup on the IP address. A big hint can be seen on the same line as the answer to the previous question.
The answer is the name of the company, not the URL. You naughty naughty trying to throw me off with the hint in the question saying not to include the “.”!

A: Host*** ***
Q7: What is the SPF record for the Return-Path domain?
First we need the domain. Run grep "Return-Path" challenge.eml and grab the domain name. Now navigate on your machine to a website that lets you do an SPF lookup (I used MXToolBox). Search for the domain and you should get the answer.
A: v=*** include:***.***.***.com -all
Q8: What is the DMARC record for the Return-Path domain?
If you’re using MXToolBox like me, then navigate over to “DMARC” using the top navbar and search for the same domain.
A: v=***; p=***; fo=1
Q9: What is the name of the attachment?
Let’s get back into the vm and run some more grep commands!
To get the name of the attachment, simply run grep "attachment" challenge.eml.
A: SWT_***_PDF.CAB
Q10: What is the SHA256 hash of the file attachment?
We could do this the easy way - open up the .eml file in ThunderBird, save the attachment, run sha256sum <attachment>. But what fun would that be? No, I want to challenge myself and do this throught the terminal. Let’s go!
> does research
> realizes that tools needed are not installed
> *vm has no internet connection*
> proceeds to accept defeat
Ok, we’re gonna do it the easy way…
A: long string of random letters and numbers… 2a91c533615a9***
Q11: What is the attachments file size? (Don’t forget to add “KB” to your answer, NUM KB)
This one threw me for a loop. I was trying to get the file size using the stat command and converting the output from bytes to KB. Wasn’t working…
But then I looked at the hint and it says you’re not supposed to do that. Instead, you’re supposed to find the file size using the hash and OSINT.
Well, in that case, let’s copy the sha256 hash we just generated and navigate over to VirusTotal. Let’s click the “search” tab and paste in the hash.
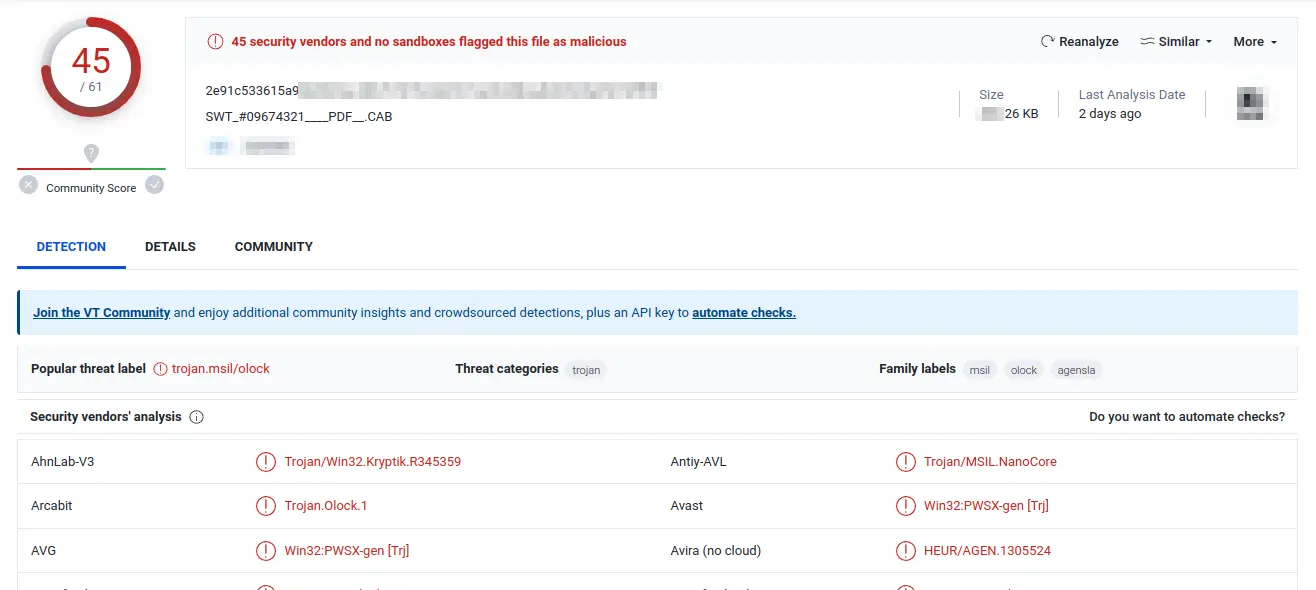
A: ***.26 KB
NOTE: Added a comment about this at the end of this post not to spoil the answer at this point.
Q12: What is the actual file extension of the attachment?
The answer can be seen on the same page on VirusTotal, but we can also navigate over to the “Details” tab to get a better idea of what the file does.
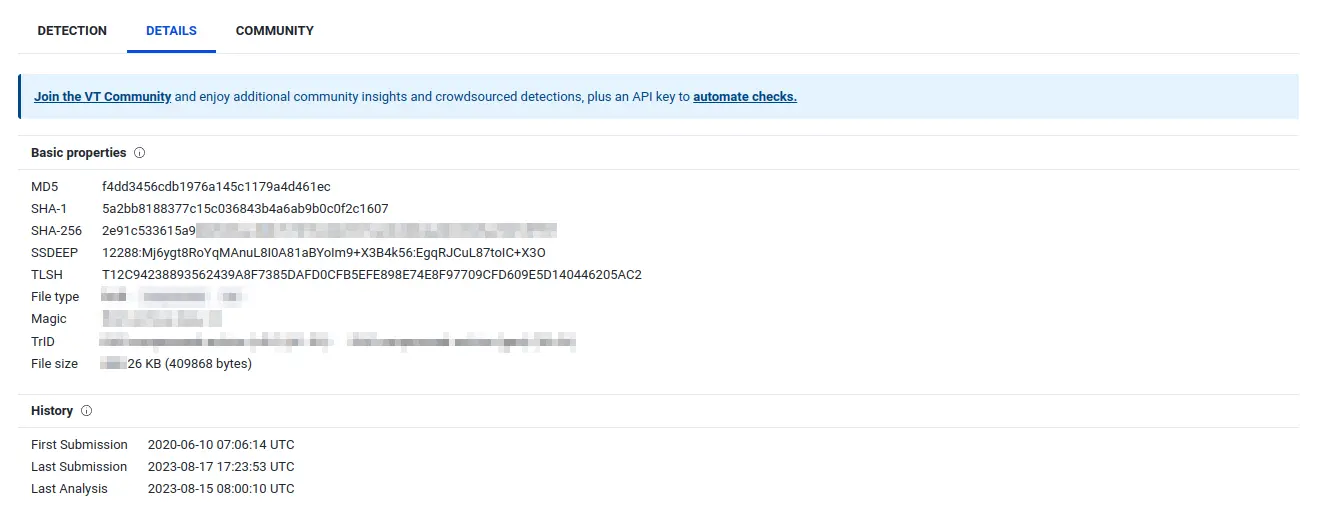
A: *A*
And there we have it! Thank you for reading my writeup of this CTF. Have a nice day! :)
Footnotes
Spoiler alert!
Comment: I feel like question 11 is somewhat misleading asking for the answer in KB, when the correct format seems to be KiB. In my case, I read “KB” as being a decimal number (power of 10) and KiB as binary (power of 2).
409868 bytes / 1000 = 409.868 kilobytes (decimal KB) while 409868 bytes / 1024 = 400.261 kibibytes (binary KiB). The value in KiB is correct but VirusTotal does also list the value as KB.¯\_(°‿°)_/¯
Oh well, this kind of confusion seems to be widespread and is a rabbithole for another time. You can read more about it on Wikipedia.
Just something to keep in mind!